Released on January 1, three years ago, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a privacy guideline aiming at delivering Californians with more governance of their private details. Companies are obliged to reflect the CCPAs regulation and user security needs in case they assemble and trade the sensitive details of citizens in the stated region.
In this article, we’ll deliver the across-the-board view of the CCPA and clarify what it implies for corporations that operate in this city.
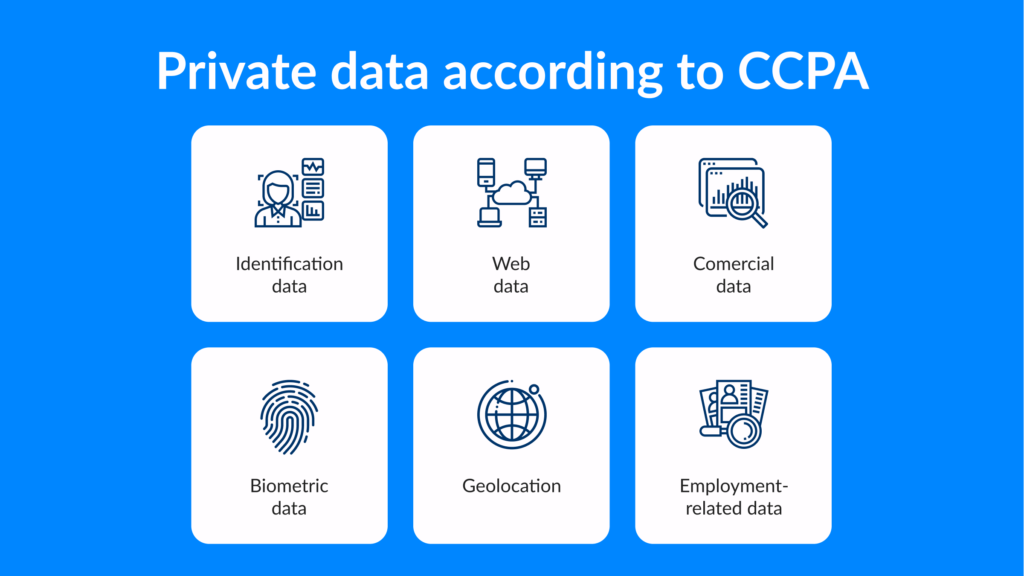
Kinds of Personal Data Protected by the CCPA
A wide range of private details is comprised into the CCPA, incorporating the following details:
- Details such as a real name, delivery information, original user identity, online identifier, IP address, email post, account name, etc.
- Aspects that are covered by legislative or California law’s defended classifications, such as race, color, religion, marital status, physical or mental health, sex, age, national origin, ancestry, or sexual orientation
- Commercial details, such as documents of commodities or services ordered, considered, or purchased, as well as other records or tendencies of consumption
- Internets or any other network activity information, such as browsing history, search history, and details of a user’s interaction with an Internet website, application, or advertisement
- Geolocation information
- Audio, electronic, visual, thermal, olfactory, or similar data
- Details that refer to a person’s career or employment history
- Education data, which is specified as details that is not publicly available personally identifiable information as d (FERPA)
What Protections Are Afforded to Consumers by the CCPA?
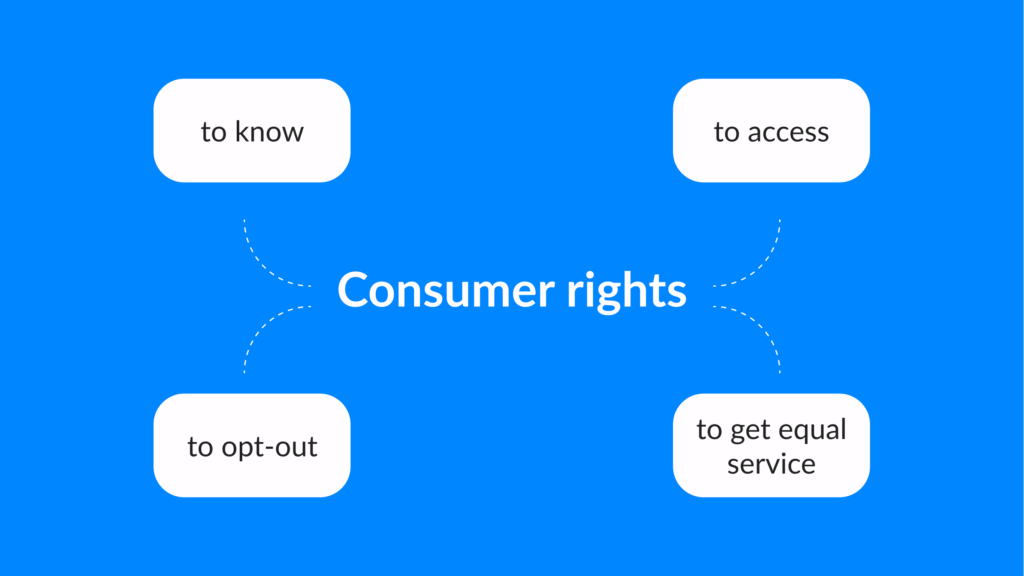
Meeting CCPA compliance, users have the following rights:
Right to know
Users have the privilege to call into question the personal details that a firm has compiled regarding them, covering the sorts of information assembled, the sources from which it was extracted, and the intentions for which it was collected.
The right to ask for deletion
Clients have the right to ask corporations to remove their private information.
Right to reject the sale of personal details
Needless to say, customers are entitled to deny the acquisition of their personal data by a business.
Right to non-discrimination
According to the CCPA act, they also may be treated fairly by businesses when they use their CCPA rights.
What Conditions Apply to Businesses Under the CCPA?
Businesses subject to the CCPA must take the next activities:
- Ensure an announcement at the time of assembly. Firms are mandated to provide a notice at the time of compilation of the classifications of personal information to be collected and the objectives to which the information will be put.
- Suggest a privacy policy. It is a must to offer a privacy policy summarizing the techniques for amassing, leveraging, and transferring client data as well as the rights that Californians have under the CCPA.
- React to customer requests
- Enterprises have 45 days to react to client information queries and removal demands.
- Implement a “Do Not Sell” button. As a market player, you should simplify it for customers to select not to have their personal data sold by implementing a “Do Not Sell” switch on your web platform or mobile application.
- Business owners must train team members on the CCPA as well as their legal duties.
- Verify consumer requests. Under the CCPA, industries are directed to assure the identity of shoppers making appeals while also taking into account the classification and sensitivity of the sought personal details.
What Sanctions Are There for Breaking the CCPA?
For purposeful violations, the CCPA allows for civil fines of up to $7,500 per violation and for inadvertent infractions, up to $2,500 per violation. Additionally, firms that violate the CCPA may be subject to enforcement actions brought by the California Attorney General, which may carry heavy fines and other penalties.
Summarize
In conclusion, the CCPA is a thorough privacy regulation that offers Californians more control over their personal data and mandates that companies give customers specific disclosures and rights. Businesses that do business in California should get familiar with the CCPA and take the necessary precautions to be in compliance. This can entail doing a review and update of their privacy policies, training staff members, and setting up procedures for handling customer demands. Businesses can safeguard themselves from potential enforcement proceedings and contribute to consumer trust-building by implementing these practices.


